Manual for api-editor#
General#
The purpose of the API-Editor is to manually annotate classes, functions, and parameters from a given API
to generate an improved API. The library-analyzer, in contrast, marks annotations automatically.
These annotations can be imported, edited and deleted in the API-Editor.
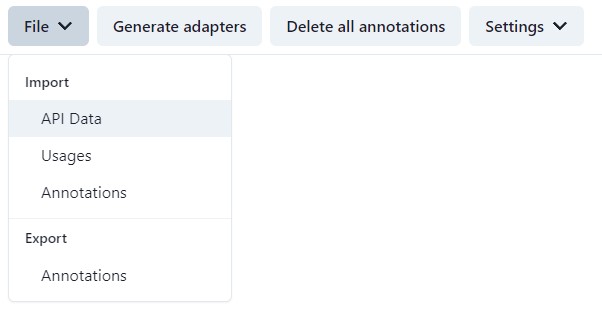
Import#
Before you can start adding own annotations, you need to import the generated API, usages and annotations files from the library-analyzer.
Now you can select packages, classes, functions, or parameters from the tree view on the right side and see the further information (documentation, annotation, etc.) about the selected element on the left side.
Annotations#
An improved API is created through annotations.
library-analyzer automatically generates some types of annotations by the documentation and the number of calls.
These are Boundary, Constant, Enum, Optional, Remove, and Required.
The other annotations cannot be generated, but are set manually with api-editor.
To add new annotations, select the corresponding class, function, or parameter in the tree view and choose the desired annotation from the drop-down menu on the left. On the right side, there is now an input for the creation of the annotation. To edit an annotation, click on the annotation in the selected component of the API, and to delete it, click on the red trash button on the right side of the annotation panel.
List of annotations and their meaning#
-
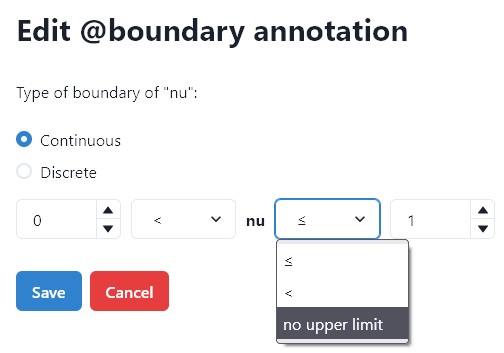
Boundary#
The annotation is used for numerical parameters, that should be in a specific range. The interval can be open or closed, and can have no upper or lower limit. Continuous or Discrete refers to the set of real numbers or integers.
-
CalledAfter#
When a function may only be called after another function, it should be marked with a CalledAfter annotation. The two functions must be in the same class.
-
Constant#
Parameters that are assigned only one value are marked with this annotation. The function `f(x, y)` where x has a constant annotation will be a local variable with the result that `f(y)` has one parameter less. Permitted types are primitive data types or None.
-
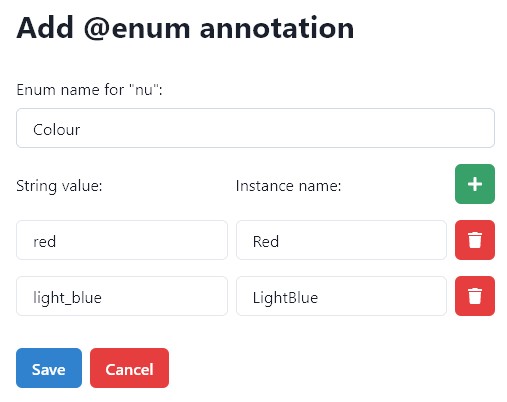
Enum#
The annotation is for string parameters that require specific words as input, and they should be converted to an enum. Its elements contain a string value which is the value of the parameter and an instance name for the name of the element.
-
Group#
A group annotation is applicable on a function, but user-defined parameters are grouped into a single parameter in the enhanced API. For that purpose, a new class with the selected parameters will be created. The list of parameters of the method will contain the not selected parameters and one from the type of the new created class.
-
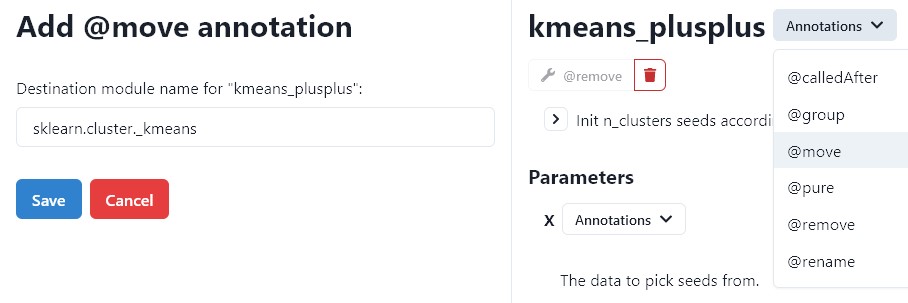
Move#
Classes with this annotation will be moved to a custom module.
-
Optional#
A new default value for the parameter should be added. e.g, The function
f(x=1)would be converted tof(x). -
Pure#
This annotation applies to functions that have no side effects and whose return value is the same if the parameters passed in the calls are the same. An invocation of such a function can be deleted if the return value isn't assigned. The second attribute allows the function to be cached.
-
Remove#
A class or a function that is marked with this annotation should be removed.
-
Rename#
This annotation renames a class, function, or parameter.
-
Required#
An optional Parameter should be required. It is the opposite action of [Optional](#optional).
Features#
There are features for a better overview of the API and its usages.
Filter#
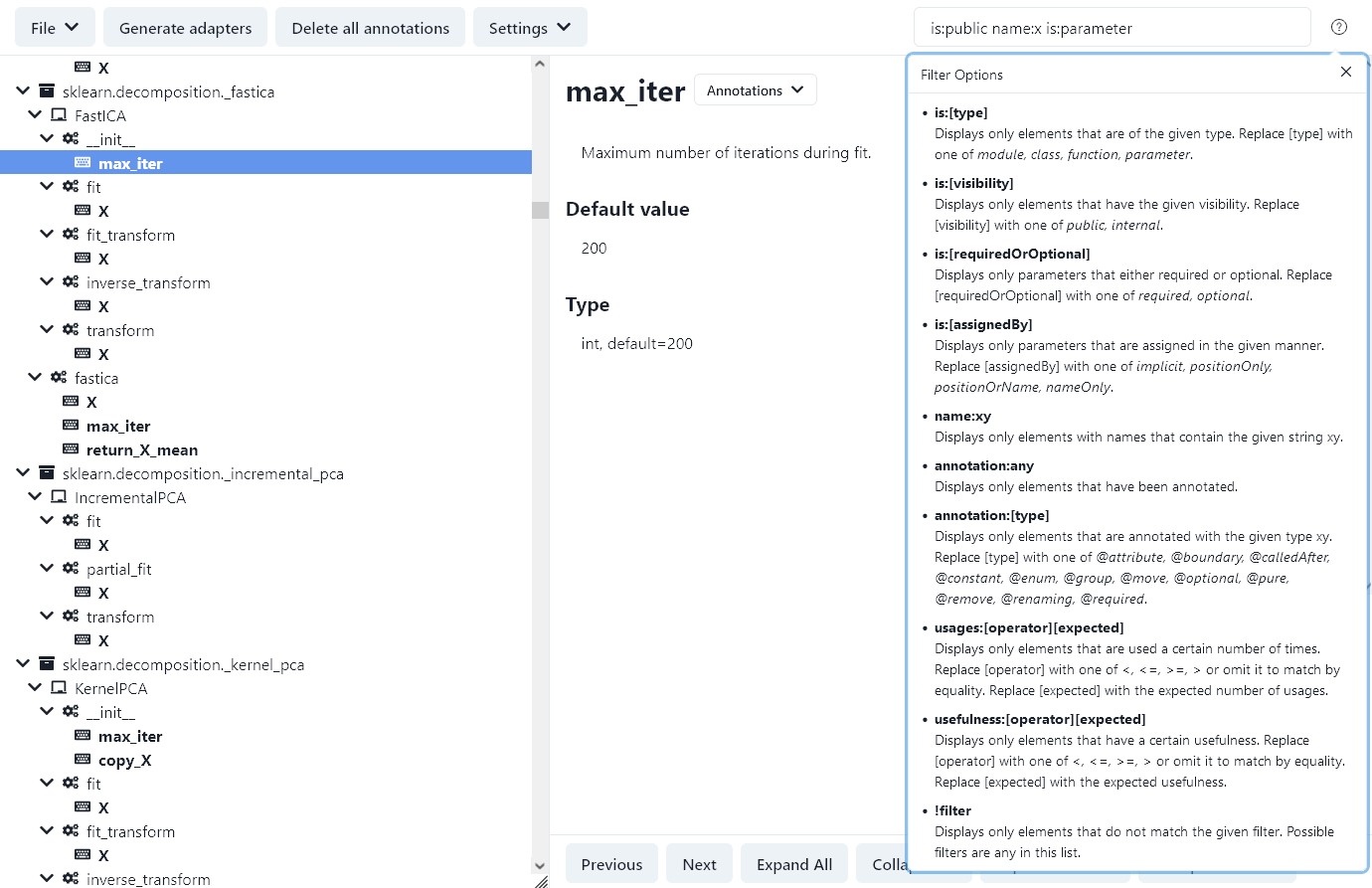
For a better listing, there is a text box filter in the top right corner that can filter the elements of the API.
The available commands for filtering are displayed when you press the help button on its right side.
If an ! is before a command, it negates that filter.
Multiple commands are interpreted as an and operation.
The elements that meet the filter are printed in bold in the tree view.
Heat Map#
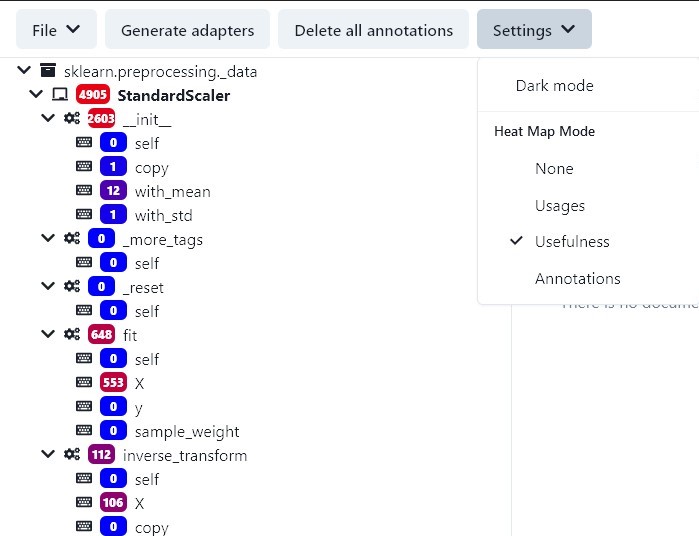
To get a heat map for the number of annotations or calls, go to Settings → Heat Map Mode and click on the desired view. There are two options for the number of times the API is used. Usages shows the total number of calls and usefullness subtract out the internal calls. The third option is for the number of annotations that a class, function, or parameter has.
In the tree view of all components of the API, the number of uses or the number of annotations of an individual component is color-coded in a box to the left of its name. The warmer the color of the box, the more often the component is used or the more annotations it has. The absolute number can be found in the box.
Navigation bar#
At the bottom right is a panel with six buttons for better handling of the tree view: Previous and Next select the previous or next item in the tree view that meet the filter. The other four buttons expand or collapse the entire tree view or only the selected element and all elements contained in it recursively.
Delete all annotations#
On the menu bar is a button to delete all annotations. Use this button wisely, or export the annotations (File → Export → Annotations) before proceeding.
Generate API#
The button Generate adapters creates the improved API. If there are any conflicts with annotations, they will be displayed and a new API won't be generated. For example, a class cannot have the annotations remove and move. One of them should be removed. After generation, you can select the folder in which the file is to be stored. It is a zip file that contains the folder adapter which contains the new API.